Code
(raw <- utils::available.packages() %>% as_tibble())How CRAN packages are interconnected
H. Sherry Zhang
2022-10-18
When writing a package, we may want to use functions in other packages. This creates a dependency for our package and a reverse dependency on the package we borrow functions from. As one of the recipients of the isoband email1, I’m curious to know how interconnected CRAN packages are. Luckily, it is not too hard to get data on this, and so the journey begins…
The utils package provides the function available.packages() to extract CRAN package information. The data includes information on the package name, version, dependency, and license:
# A tibble: 18,692 × 17
Package Version Priority Depends Imports Linki…¹ Sugge…² Enhan…³ License
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
1 A3 1.0.0 <NA> R (>= 2… <NA> <NA> random… <NA> GPL (>…
2 AATtools 0.0.2 <NA> R (>= 3… magrit… <NA> <NA> <NA> GPL-3
3 ABACUS 1.0.0 <NA> R (>= 3… ggplot… <NA> rmarkd… <NA> GPL-3
4 abbreviate 0.1 <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA> testth… <NA> GPL-3
5 abbyyR 0.5.5 <NA> R (>= 3… httr, … <NA> testth… <NA> MIT + …
6 abc 2.2.1 <NA> R (>= 2… <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA> GPL (>…
7 abc.data 1.0 <NA> R (>= 2… <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA> GPL (>…
8 ABC.RAP 0.9.0 <NA> R (>= 3… graphi… <NA> knitr,… <NA> GPL-3
9 abcADM 1.0 <NA> <NA> Rcpp (… Rcpp, … <NA> <NA> GPL-3
10 ABCanalysis 1.2.1 <NA> R (>= 2… plotrix <NA> <NA> <NA> GPL-3
# … with 18,682 more rows, 8 more variables: License_is_FOSS <chr>,
# License_restricts_use <chr>, OS_type <chr>, Archs <chr>, MD5sum <chr>,
# NeedsCompilation <chr>, File <chr>, Repository <chr>, and abbreviated
# variable names ¹LinkingTo, ²Suggests, ³EnhancesFrom this, we can extract a table to map out the direct dependency every CRAN package has. In this post we will focus on the two strong dependencies: Depends and Imports:
all_pkgs <- raw %>%
tidyr::separate_rows(Imports, sep = ",") %>%
tidyr::separate_rows(Depends, sep = ",") %>%
mutate(
across(c(Depends, Imports), ~gsub("\\(.*\\)", "\\1", .x)),
across(c(Depends, Imports), str_trim)
)
# filter(!Depends %in% c("R", ""), Imports != "", !is.na(Depends))
(dep_lookup_tbl <- all_pkgs %>%
dplyr::select(Package, Depends, Imports) %>%
rename(downstream = Package) %>%
pivot_longer(Depends:Imports, names_to = "type", values_to = "upstream") %>%
distinct() %>%
filter(!upstream %in% c("R", "")) %>%
filter(!is.na(upstream)) %>%
arrange(downstream))# A tibble: 96,765 × 3
downstream type upstream
<chr> <chr> <chr>
1 A3 Depends xtable
2 A3 Depends pbapply
3 AATtools Imports magrittr
4 AATtools Imports dplyr
5 AATtools Imports doParallel
6 AATtools Imports foreach
7 ABACUS Imports ggplot2
8 ABACUS Imports shiny
9 ABC.RAP Imports graphics
10 ABC.RAP Imports stats
# … with 96,755 more rowsDependency is a transitive relation. This means a package also (indirectly) depends on all the dependencies of the package of it imports and so on. Changes from an package will propagate downwards through its dependency chain. With the direct dependency table above, we can iteratively construct the extended dependency tree:
find_all_deps <- function(upstream, data){
print(upstream)
dt <- tibble()
dt2 <- data
i <- 1
while(nrow(dt2) > nrow(dt)){
print(i)
dt <- dt2
n <- paste0("upstream", i)
dt2 <- dt %>%
rename(upstream = downstream) %>%
left_join(dep_lookup_tbl %>% select(-type), by = "upstream") %>%
rename(!!quo_name(n) := upstream)
i <- i + 1
}
dep <- dt2 %>%
pivot_longer(
cols = c(contains("upstream"), "downstream"),
names_to = "dump", values_to = "downstream") %>%
distinct(downstream) %>%
filter(!is.na(downstream)) %>%
mutate(downstream = sort(downstream))
return(dep)
}
dep_all <- dep_lookup_tbl %>%
arrange(-desc(upstream)) %>%
nest(direct_deps = -upstream) %>%
mutate(all_deps = map2(upstream, direct_deps, find_all_deps))
(edges <- dep_all %>%
select(-direct_deps) %>%
unnest(all_deps) %>%
filter(!is.na(upstream), !is.na(downstream)))# A tibble: 551,713 × 2
upstream downstream
<chr> <chr>
1 a4Core nlcv
2 abc abctools
3 abc EasyABC
4 abc ecolottery
5 abc nlrx
6 abc paleopop
7 abc poems
8 abc.data abc
9 abc.data abctools
10 abc.data EasyABC
# … with 551,703 more rowsThe plot below shows the number of dependencies and reverse dependencies a package has.
nodes <- tibble(id = unique(c(edges$upstream, edges$downstream))) %>%
left_join(edges %>% count(upstream, name = "n_revdep"), by = c("id" = "upstream")) %>%
left_join(edges %>% count(downstream, name = "n_dep"), by = c("id" = "downstream")) %>%
filter(!is.na(id)) %>%
mutate(n_revdep = ifelse(is.na(n_revdep), 0, n_revdep),
n_dep = ifelse(is.na(n_dep), 0, n_dep))
################################################################
# deriving color categories
recommended <- raw %>% filter(Priority == "recommended") %>% pull(Package)
base <- c("base", "compiler", "datasets", "grDevices", "graphics", "grid", "methods", "parallel", "splines", "stats", "stats4", "tcltk", "tools", "translations", "utils")
r_lib_gh <- gh("GET /orgs/{username}/repos", username = "r-lib", .limit = 200)
r_lib <- vapply(r_lib_gh, "[[", "", "name")
r_tidyverse_gh <- gh("GET /orgs/{username}/repos", username = "tidyverse", .limit = 40)
tidyverse <- vapply(r_tidyverse_gh, "[[", "", "name")
nodes <- nodes %>%
mutate(category =
case_when(id %in% tidyverse ~ "tidyverse",
id %in% base ~ "base",
id %in% r_lib ~ "r-lib",
id %in% recommended ~ "recommended",
TRUE ~ "zzz"))
################################################################
# to deal with zero mark after sqrt tranform
# https://github.com/tidyverse/ggplot2/issues/980
mysqrt_trans <- function() {
scales::trans_new("mysqrt",
transform = base::sqrt,
inverse = function(x) ifelse(x<0, 0, x^2),
domain = c(0, Inf))
}
p <- nodes %>%
mutate(tooltip = glue::glue("Pkg: {id}, dep: {n_dep}, revdep: {n_revdep}")) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = n_dep, y = n_revdep)) +
geom_point_interactive(aes(tooltip = tooltip)) +
ggrepel::geom_text_repel(
data = nodes %>% filter(n_revdep > 3100),
aes(color= category, label = id), min.segment.length = 0) +
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Set1") +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = c(0, 50, 200, 500, 1000, 2500, 5000, 7500, 10000, 15000), trans = "mysqrt") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = c(0, 1, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 120, 160, 200), trans = "mysqrt") +
theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),
legend.position = "bottom") +
xlab("Number of dependencies") +
ylab("Number of reverse dependencies")
girafe(ggobj = p, width_svg = 16, height_svg = 12)The x and y-axes show the number of dependencies and reverse dependencies of a package. Both coordinates are square root transformed to accommodate for the skewness in both measures. Packages with more than 3100 reverse dependencies are labelled. The label color denotes four groups: those in base R, those labelled as “recommended” by CRAN, and those listed in the tidyverse and r-lib organisations on GitHub. Expand the color group below to view the package membership:
color group
| category | packages |
|---|---|
| base | base, compiler, datasets, graphics, grDevices, grid, methods, parallel, splines, stats, stats4, tcltk, tools, utils |
| tidyverse | blob, dbplyr, dplyr, dtplyr, forcats, ggplot2, glue, googledrive, googlesheets4, haven, hms, lubridate, magrittr, modelr, multidplyr, nycflights13, purrr, readr, readxl, reprex, rvest, stringr, tibble, tidyr, tidyverse, vroom |
| r-lib | archive, askpass, available, backports, bench, brio, cachem, callr, carrier, cli, clisymbols, clock, commonmark, conflicted, coro, covr, cpp11, crayon, credentials, debugme, desc, devtools, downlit, ellipsis, err, evaluate, fastmap, filelock, fs, gargle, generics, gert, gh, gitcreds, gmailr, gtable, here, httr, httr2, jose, keyring, later, lifecycle, lintr, liteq, lobstr, memoise, mockery, pak, pillar, pingr, pkgbuild, pkgcache, pkgconfig, pkgdepends, pkgdown, pkgload, prettycode, prettyunits, processx, progress, ps, R6, ragg, rappdirs, rcmdcheck, rematch2, remotes, rex, rlang, roxygen2, rprojroot, scales, sessioninfo, showimage, sodium, styler, svglite, systemfonts, testthat, textshaping, tidyselect, tzdb, urlchecker, usethis, vctrs, waldo, whoami, withr, xml2, xmlparsedata, xopen, ymlthis, zeallot, zip, roxygen2md, diffviewer, vdiffr, asciicast, cliapp, decor, meltr, sloop, tracer, io, conf, webfakes |
| recommended | boot, class, cluster, codetools, foreign, KernSmooth, lattice, MASS, Matrix, mgcv, nlme, nnet, rpart, spatial, survival |
The plot is interactive so you can hover over points of your interest to read the package name and its numbers of (reverse) dependency.
As you would have already noticed, the distribution of the number of reverse dependencies is highly skewed, even after the square root transformation. To better visualise how the lower number of reverse dependency is distributed, we can plot its cumulative distribution:
prct_tbl <- purrr::map_dfr(
unique(nodes$n_revdep) %>% sort(),
~tibble(n = .x, prct = nrow(filter(nodes, n_revdep <= .x)) /nrow(nodes)))
tgt_pnts <- prct_tbl %>%
mutate(p = round(prct, digits = 3)) %>%
filter(p %in% c(0.9, 0.95, 0.99, 0.995, 0.999) | prct == 1 |n %in% c(0, 1, 5)) %>%
group_by(p) %>%
filter(n == min(n))
prct_tbl %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x = n, y = prct)) +
geom_point(data = tgt_pnts, aes(x = n, y = prct)) +
geom_label(data = tgt_pnts, aes(x = n, y = prct + 0.01, label = p)) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = round(c(tgt_pnts$n, max(prct_tbl$n)))) +
coord_trans("pseudo_log") +
theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank()) +
ylab("Percentage of CRAN pkgs with <= n reverse dependencies")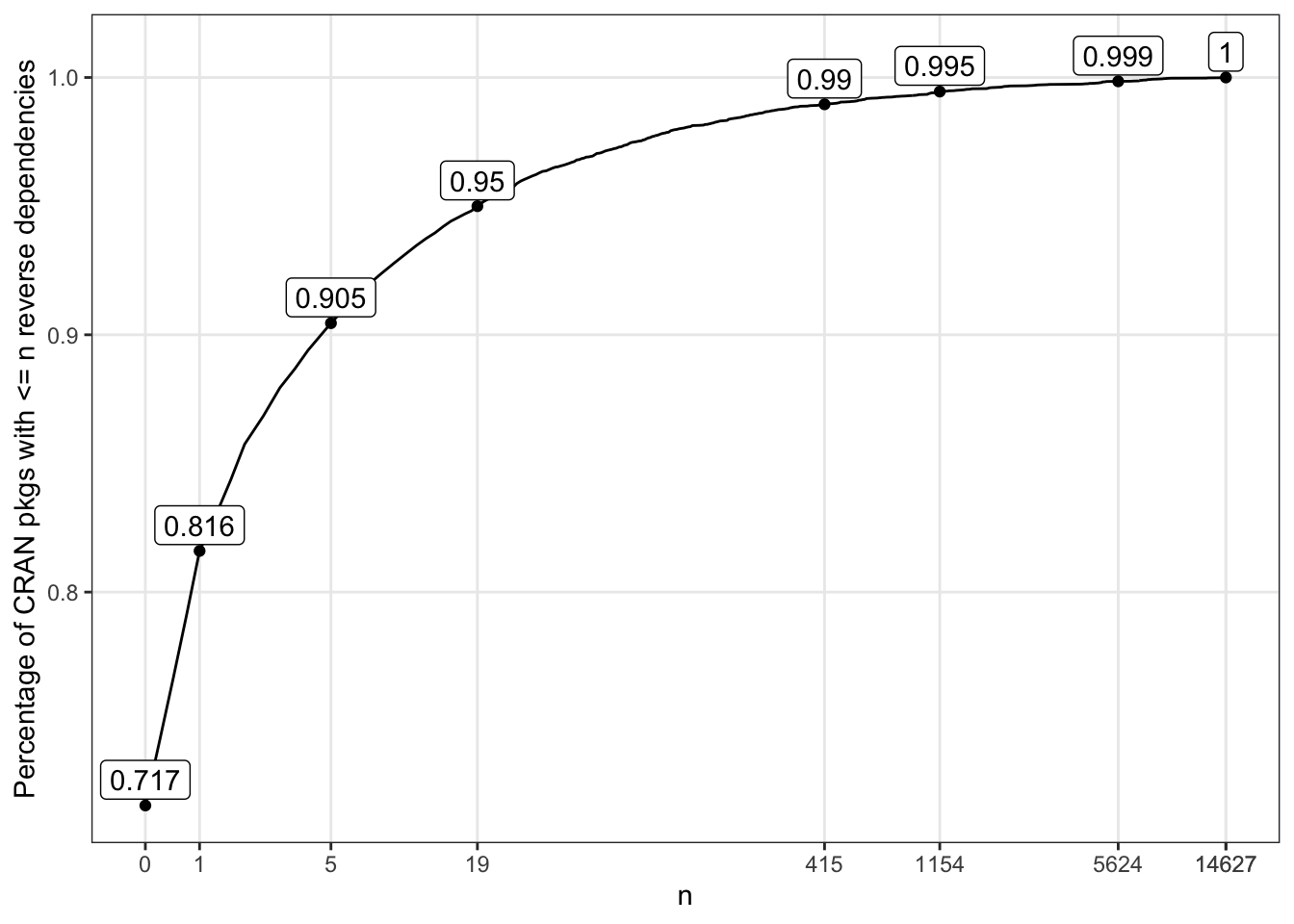
Whether you have guessed or not:
So while the majority of the R packages do not need reverse dependency checks, a small number of core packages need to test against hundreds or even thousands of reverse dependencies for every new release.
Alternatively, we can rank the packages by their number reverse dependencies (the package with the largest number of reverse dependencies is ranked first). The advantage of this is that there turns out to be a distribution that can capture the shape well: the Zipf–Mandelbrot distribution, the generalised zipf distribution, which is commonly used to model corpus frequency in linguistics:
nodes_rank <- nodes %>%
mutate(rank = rank(-n_revdep, ties.method = "first")) %>%
filter(n_revdep > 0)
dt_pos <- nodes %>% filter(n_revdep > 0) %>% pull(n_revdep) %>% sort(decreasing = TRUE)
pred1 <- fitrad(dt_pos, "mand") %>% radpred()
fitted <- tibble(
rank = pred1$rank,
mand = pred1$abund,
count = dt_pos)
p2 <- nodes_rank %>%
ggplot(aes(x = rank, y = n_revdep)) +
geom_point_interactive(aes(tooltip = id)) +
geom_line(data = fitted, aes(x = rank, y = mand), color = "#314f40") +
ggrepel::geom_text_repel(
data = nodes_rank %>% filter(n_revdep > 3100),
aes(label = id, color = category),
min.segment.length = 0) +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = c(10, 50, 200, 500, 1000, 2500, 5000, 7500, 10000, 15000)) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = c(0, 1, 10, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000, 20000)) +
coord_trans(x = "log", y = "sqrt") +
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Set1") +
theme_bw() +
theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),
legend.position = "bottom") +
ylab("number of reverse dependencies")
girafe(ggobj = p2, width_svg = 16, height_svg = 12)We can also find packages with similar characteristics as isoband: those with a huge number of reverse dependencies (n > 3000) while not managed by base R or RStudio or listed as recommended on CRAN:
| Package | # of reverse dependency |
|---|---|
| Rcpp | 8401 |
| fansi | 6777 |
| utf8 | 6777 |
| digest | 6418 |
| colorspace | 5041 |
| RColorBrewer | 5030 |
| viridisLite | 4895 |
| farver | 4875 |
| labeling | 4865 |
| munsell | 4864 |
| stringi | 4573 |
| jsonlite | 4326 |
| yaml | 3031 |
| mime | 3020 |
In a quick glance, these packages fall into three categories:
colorspace, RColorBrewer, viridisLite, munsellRcpp for interfacing to C++ for fast computation;jsonlite for parsing JSON; andstringi for string manipulation.ggplot2:
digest for hashing object in R, andfarver and labelling are imported by scales, which in turn is imported by ggplot2tibble:
fansi for ANSI text formatting, andutf8 for processing UTF encoding, imported by pillar, which is imported by tibbleshiny: mime for converting file name extension, andknitr: yaml for YAML text conversionFinally, the network diagram! I have tried to include all 17,354 nodes and 551,713 pairs of edges in a single diagram and I do not blame my computer for rejecting it with
vector memory exhausted (limit reached?). To avert this error, I plot a subset of the large number of packages with n ≤ 5 reverse dependencies. Specifically, for each n ≤ 5, I randomly select 40 packages with the given n. After playing around with layouts and other aesthetics, here is the result…
code
wirdos <- c("brglm", "profileModel", "ExPosition", "prettyGraphs", "seasonal", "x13binary", "scalreg", "lars", "elasticnet")
more_than5 <- nodes %>% filter(n_revdep > 5) %>% filter(!id %in% wirdos)
set.seed(123)
less_than5 <- nodes %>%
filter(n_revdep <= 5) %>%
nest_by(n_revdep, .key = "nested") %>%
mutate(id = list(map(nested, ~sample(.x, size = 40))$id)) %>%
unnest(id) %>%
select(-nested) %>%
ungroup()
new_nodes <- bind_rows(more_than5, less_than5)
new_edges <- dep_lookup_tbl %>% filter(upstream %in% new_nodes$id & downstream %in% new_nodes$id) %>% select(-type)
new_nodes <- new_nodes %>% filter(id %in% c(new_edges$downstream, new_edges$upstream))
g <- tbl_graph(nodes = new_nodes, edges = new_edges, directed = TRUE)
ggraph(g, layout = "fr") +
geom_edge_link(alpha = 0.1) +
geom_node_label(data = ~ .x %>% filter(n_revdep >= 3200), aes(label =id), repel = TRUE) +
geom_node_point(aes(size = n_revdep), alpha = 0.5) +
theme_void() +
theme(legend.position = "none")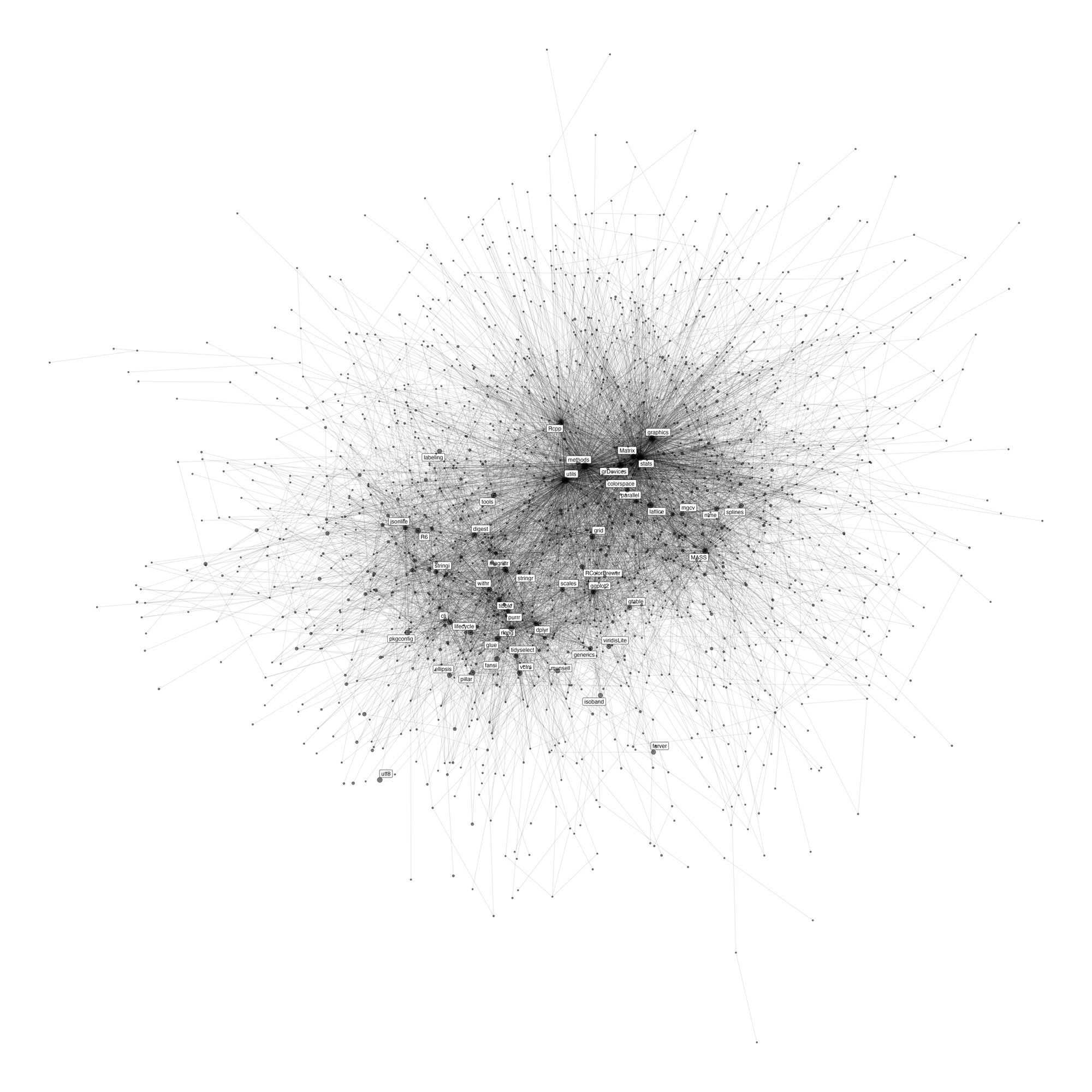
On 5th Oct, CRAN sent out a massive email to inform 4747 downstream package maintainers of the potential archive of package isoband on 2022-10-19.↩︎